
Over the past four years, many Americans have found themselves increasingly burdened by debt.
This troubling trend is largely attributed to the persistent rise in inflation and the resultant escalation in living expenses. As the cost of everyday necessities climbs, more individuals are resorting to lines of credit to make ends meet, leading to a deeper entrenchment in financial liabilities.
The Inflation Surge
Inflation, the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power, has been on an upward trajectory.
Over the past few years, various factors have contributed to this surge, including supply chain disruptions, increased consumer demand, and global economic instability. As a result, the cost of essentials such as food, housing, and healthcare has soared, stretching household budgets to their limits.
Chart – US Inflation Rate
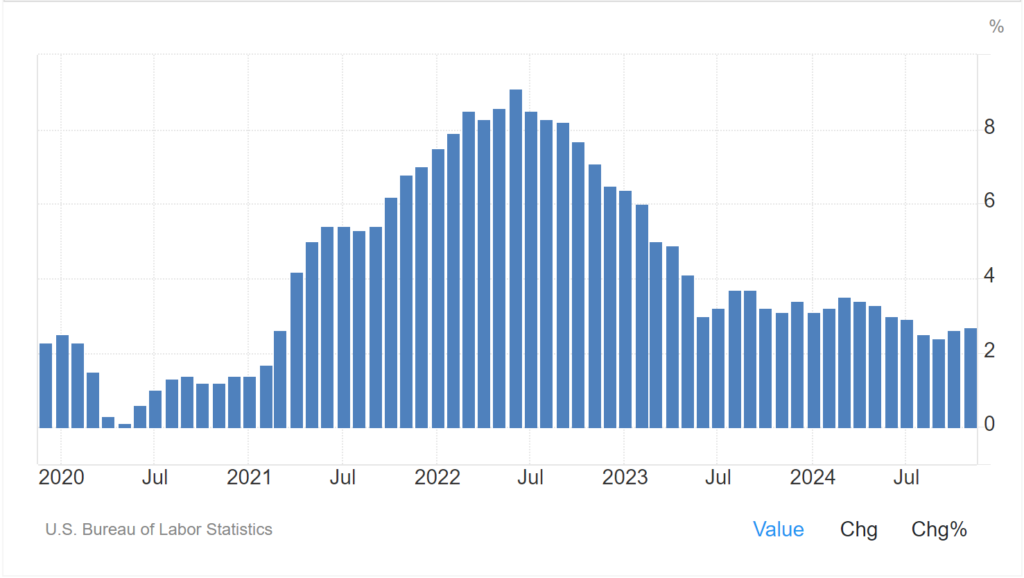
The Impact on Living Expenses
The spike in inflation has significantly impacted living expenses. Housing costs, both in terms of home prices and rental rates, have seen substantial increases. Food prices have also surged, with grocery bills becoming noticeably heftier. Additionally, the cost of healthcare and utilities has risen, further straining the financial resources of many families. These cumulative increases have forced individuals to adjust their spending habits, often at the expense of savings and long-term financial security.
United States Food Inflation
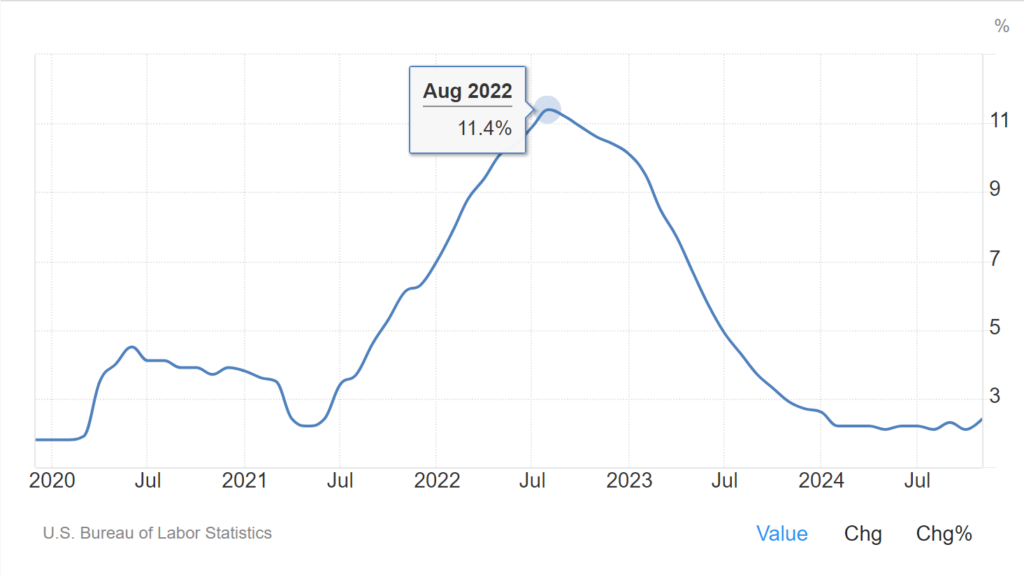
Food price inflation in the US rose to 2.4% in November 2024, the most in ten months, up from 2.1% in the prior month. Prices accelerated for food at home (1.6% vs 1.1% in October) but eased somewhat for food away from home (3.6% vs 3.8%). On a monthly basis, food prices rose by 0.4% in November, after a 0.2% increase in the prior month. source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
United States Energy Inflation
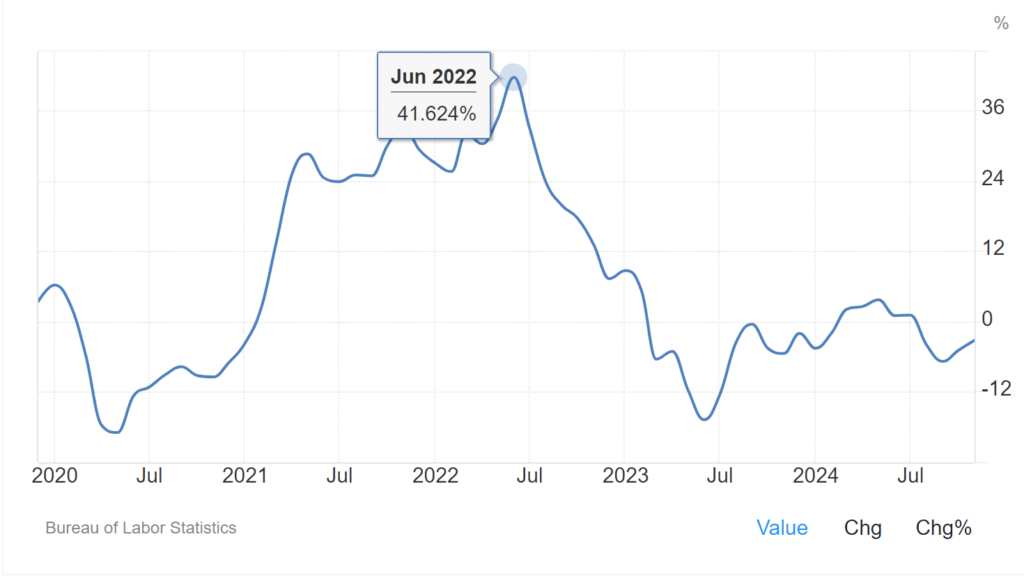
The energy index in the US fell by 3.2% over the past 12 months in November 2024, following a 4.9% decline in the prior month, marking the fourth consecutive month of decreases. Softer declines were observed in fuel oil prices (-19.5% compared to -20.8% in October) and gasoline prices (-8.1% vs. -12.2%), while the price increases for utility gas service (1.8% vs. 2%) and electricity (3.1% vs. 4.5%) moderated. On a monthly basis, energy prices rose by 0.2% in November after being flat in the prior month. source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Role of Credit
In response to these financial pressures, many Americans have turned to credit to bridge the gap between their income and expenses.
Credit cards, personal loans, and home equity lines of credit have become essential tools for covering daily costs. However, this reliance on credit has led to a significant increase in household debt levels. According to recent data, consumer debt in the United States has reached record highs, with credit card balances and personal loans contributing heavily to this figure.
United States Debt Balance Credit Cards
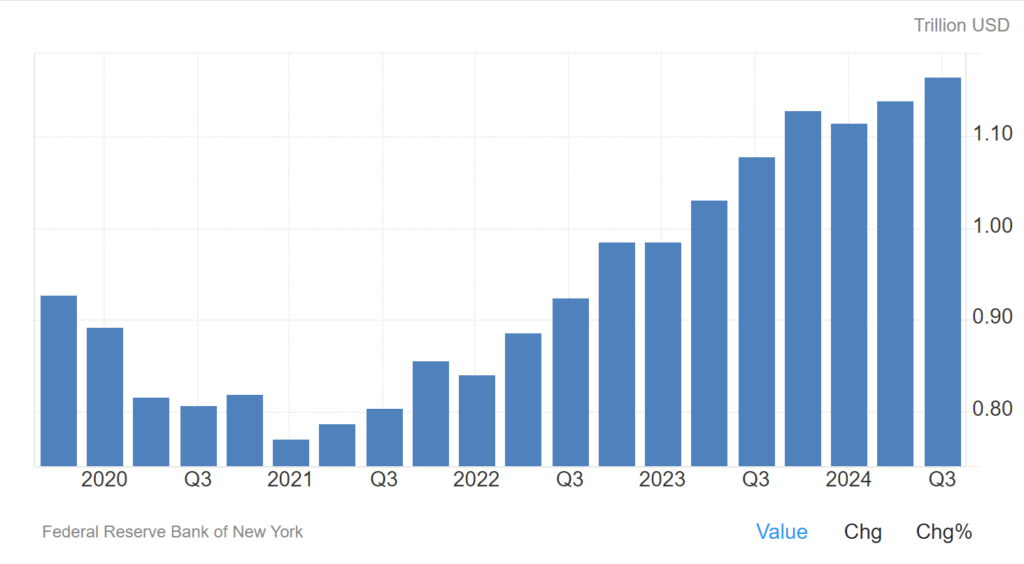
Debt Balance Credit Cards in the United States increased to 1.17 Trillion USD in the third quarter of 2024 from 1.14 Trillion USD in the second quarter of 2024. Debt Balance Credit Cards in the United States averaged 0.79 Trillion USD from 2003 until 2024, reaching an all time high of 1.17 Trillion USD in the third quarter of 2024 and a record low of 0.66 Trillion USD in the first quarter of 2014. source: Federal Reserve Bank of New York
The Debt Cycle
The reliance on credit to manage living expenses creates a challenging cycle.
High-interest rates on credit cards and loans mean that the cost of borrowing can quickly escalate. As individuals struggle to pay off existing debt, they may find themselves needing to take on additional credit to cover new expenses, perpetuating a cycle of debt that becomes increasingly difficult to break.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of this rising debt are profound. High debt levels can negatively impact credit scores, making it harder for individuals to access affordable credit in the future. It can also limit the ability to save for retirement, invest in education, or purchase a home, all of which are crucial components of financial stability and growth. Moreover, the psychological stress of carrying significant debt can affect overall well-being and mental health.

Navigating the Crisis
To navigate this financial crisis, individuals must take proactive steps. For individuals, creating a budget, prioritizing debt repayment, and seeking financial counseling can be effective strategies.
The past four years have highlighted the vulnerability of American finances in the face of rising inflation and living expenses. As more individuals find themselves deeper in debt, it is crucial to recognize the underlying causes and work towards sustainable solutions.
Get Financial Peace.
Inquire about Great White Financial’s personal and business budgeting services.









